













When talking about an ethnic group or ethnically differentiated peoples, we must link such concept
either to a territory as the essential basis of their culture, spiritual life, integrity, and autonomous
development, or to the awareness these peoples have regarding their practices, whether they are real
or symbolic, that are associated with the understanding of their nomadism. Such practices are critical
since they have guaranteed the rights that have to do with their physical and cultural survival and have
enabled them to move throughout the national territory freely.
Hence, the territorial perspective of ethnically differentiated peoples depends on the way each collective ethnic subject understands what their daily existence is contained in that is, in turn, involved with their:












Most ethnic groups require the territory they are settled in to survive and develop their culture. This acknowledgment would grant these peoples the right to collective property over those traditional territories they have lived in and make up their ancestral territories.
When talking about an ethnic group or ethnically differentiated peoples, we must link such concept either to a territory as the essential basis of their culture, spiritual life, integrity, and autonomous development, or to the awareness these peoples have regarding their practices, whether they are real or symbolic, that are associated with the understanding of their nomadism. Such practices are critical since they have guaranteed the rights that have to do with their physical and cultural survival and have enabled them to move throughout the national territory freely.
Hence, the territorial perspective of ethnically differentiated peoples depends on the way each collective ethnic subject understands what their daily existence is contained in that is, in turn, involved with their:













Most ethnic groups require the territory they are settled in to survive and develop their culture. This acknowledgment would grant these peoples the right to collective property over those traditional territories they have lived in and make up their ancestral territories.
Hence, the territorial perspective of ethnically differentiated peoples depends on the way each collective ethnic subject understands what their daily existence is contained in that is, in turn, involved with their:













Most ethnic groups require the territory they are settled in to survive and develop their culture. This acknowledgment would grant these peoples the right to collective property over those traditional territories they have lived in and make up their ancestral territories.




For this community, also referred to as gypsies, the concept of territory is understood differently. This community deems essential the concept of territorialism rather than a territory. This community that has spread its presence worldwide attaches great importance to the capacity to take possession of land and make it habitable since they settle in the territory they get. This land appropriation is coherent with their libertarian mindset commonly linked to their characteristic mobility.




Consequently, this community shapes its identity and enriches its territorial understanding as it travels around the world. They make their own pathway as they go.




For this community, the idea of living freely (nomadic lifestyle) contrasts the tradition of settling up in just one place during their lifespan. Hence, from this perspective, it is impossible to shape collective property within the borders of an exclusive territory. This concept is behind their border conceptualization that usually controls and limits those “gadze” or non-Rom.
Los territorios rurales bases de la construcción son los consejos comunitarios de comunidades negras:




For this community, also referred to as gypsies, the concept of territory is understood differently. This community deems essential the concept of territorialism rather than a territory. This community that has spread its presence worldwide attaches great importance to the capacity to take possession of land and make it habitable since they settle in the territory they get. This land appropriation is coherent with their libertarian mindset commonly linked to their characteristic mobility.




Consequently, this community shapes its identity and enriches its territorial understanding as it travels around the world. They make their own pathway as they go.




For this community, the idea of living freely (nomadic lifestyle) contrasts the tradition of settling up in just one place during their lifespan. Hence, from this perspective, it is impossible to shape collective property within the borders of an exclusive territory. This concept is behind their border conceptualization that usually controls and limits those “gadze” or non-Rom.




For this community, also referred to as gypsies, the concept of territory is understood differently. This community deems essential the concept of territorialism rather than a territory. This community that has spread its presence worldwide attaches great importance to the capacity to take possession of land and make it habitable since they settle in the territory they get. This land appropriation is coherent with their libertarian mindset commonly linked to their characteristic mobility.




For this community, the idea of living freely (nomadic lifestyle) contrasts the tradition of settling up in just one place during their lifespan. Hence, from this perspective, it is impossible to shape collective property within the borders of an exclusive territory. This concept is behind their border conceptualization that usually controls and limits those “gadze” or non-Rom.




Consequently, this community shapes its identity and enriches its territorial understanding as it travels around the world. They make their own pathway as they go.




Indigenous territories refer to those areas owned permanently and regularly by part of or a whole indigenous community. Sometimes, these territories may also refer to those territories that, even if not owned by an indigenous community, are key for developing such communities’ social, economic, and cultural activities.








As to favor the protection of the indigenous community’s territories, the National Constitution includes the collective ownership of land concept in articles 63 and 329. According to these articles, communal lands are collectively owned and are inalienable, imprescriptible, and nonforfeitable.
Los territorios rurales bases de la construcción son los consejos comunitarios de comunidades negras:




Se define como territorio indígena a las áreas poseídas en forma regular y permanente por una comunidad, parcialidad o grupo indígena y aquellas que, aunque no son no se encuentran poseídas en esa forma, constituyen el ámbito tradicional de sus actividades sociales, económicos y culturales.








Para proteger los territorios de los pueblos indígenas, la Constitución acoge el concepto de propiedad colectiva sobre la tierra en los artículos 63 y 329, estableciendo que hay tierras comunales que son de propiedad colectiva y tienen el carácter de ser inalienables, imprescriptibles e inembargables.




Se define como territorio indígena a las áreas poseídas en forma regular y permanente por una comunidad, parcialidad o grupo indígena y aquellas que, aunque no son no se encuentran poseídas en esa forma, constituyen el ámbito tradicional de sus actividades sociales, económicos y culturales.




Para proteger los territorios de los pueblos indígenas, la Constitución acoge el concepto de propiedad colectiva sobre la tierra en los artículos 63 y 329, estableciendo que hay tierras comunales que son de propiedad colectiva y tienen el carácter de ser inalienables, imprescriptibles e inembargables.




Los resguardos indígenas son una institución legal y sociopolítica de carácter especial que, junto con los territorios tienen el carácter de derecho fundamental, porque tanto resguardos como territorios constituyen el principal medio de subsistencia sino también, porque forman parte de su cosmovisión y religiosidad.
Indigenous reservations are legal and socio-political institutions holding a unique nature that, together with the territories, are understood as fundamental rights. Both reservations and territories constitute the primary means of subsistence of these communities, and they are also a key part of their worldview and religiosity.




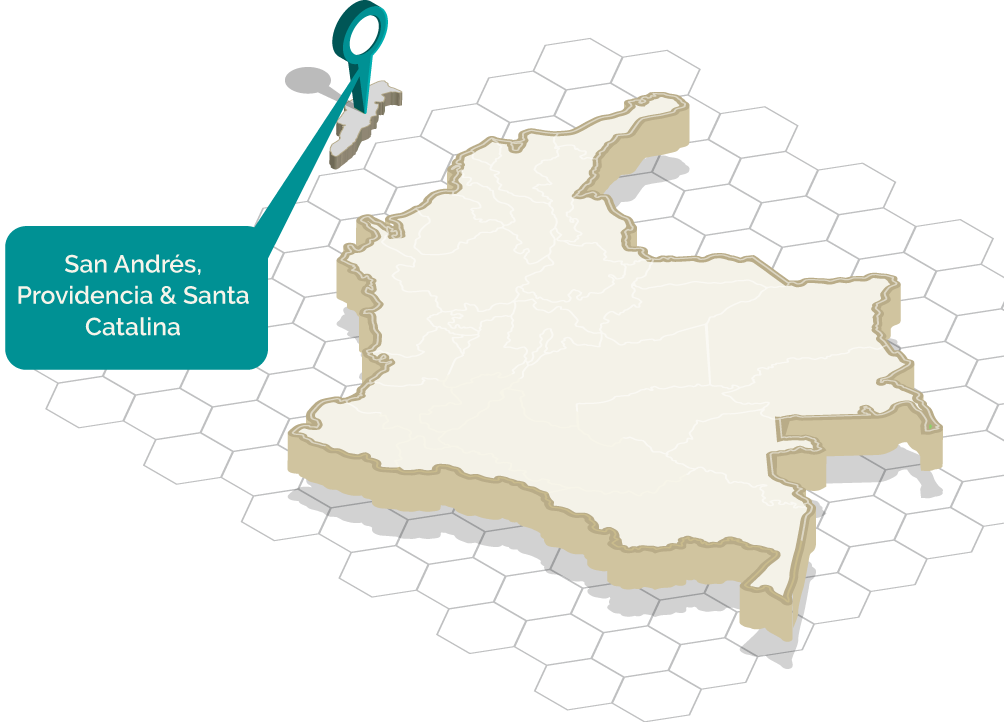
It refers to the native population from the Colombian island territories, including San Andres, Providencia, and Santa Catalina. They are descendants of European ancestors (mainly English, Dutch, and Spanish) and African slaves who inhabited these islands.







They are characterized by their culture, language (Creole), religious beliefs (baptists), and their west-Indian-like histories, like Jamaica and Haiti’s.




It refers to the native population from the Colombian island territories, including San Andres, Providencia, and Santa Catalina. They are descendants of European ancestors (mainly English, Dutch, and Spanish) and African slaves who inhabited these islands.







They are characterized by their culture, language (Creole), religious beliefs (baptists), and their west-Indian-like histories, like Jamaica and Haiti’s.




It refers to the native population from the Colombian island territories, including San Andres, Providencia, and Santa Catalina. They are descendants of European ancestors (mainly English, Dutch, and Spanish) and African slaves who inhabited these islands.




Se caracterizan por su cultura, lengua (creole), creencias religiosas (iglesia bautista) y pasado histórico similar al de pueblos antillanos como Jamaica y Haití.






They understand a territory as a concept made up of lands, waters, flora, fauna, and natural resources that provide material resources and vital support to the communities that inhabit it and interact with it.







The survival of black and Afro-Colombian communities implies the effective exercise of collective law over their territories due to the close cultural relationship with their territories.




They understand a territory as a concept made up of lands, waters, flora, fauna, and natural resources that provide material resources and vital support to the communities that inhabit it and interact with it.







The survival of black and Afro-Colombian communities implies the effective exercise of collective law over their territories due to the close cultural relationship with their territories.




They understand a territory as a concept made up of lands, waters, flora, fauna, and natural resources that provide material resources and vital support to the communities that inhabit it and interact with it.




The survival of black and Afro-Colombian communities implies the effective exercise of collective law over their territories due to the close cultural relationship with their territories.
The underlying territories of the construction of the culture and identity of these communities are called community councils. So far, the following councils have been identified:
The underlying territories of the construction of the culture and identity of these communities are called community councils. So far, the following councils have been identified:
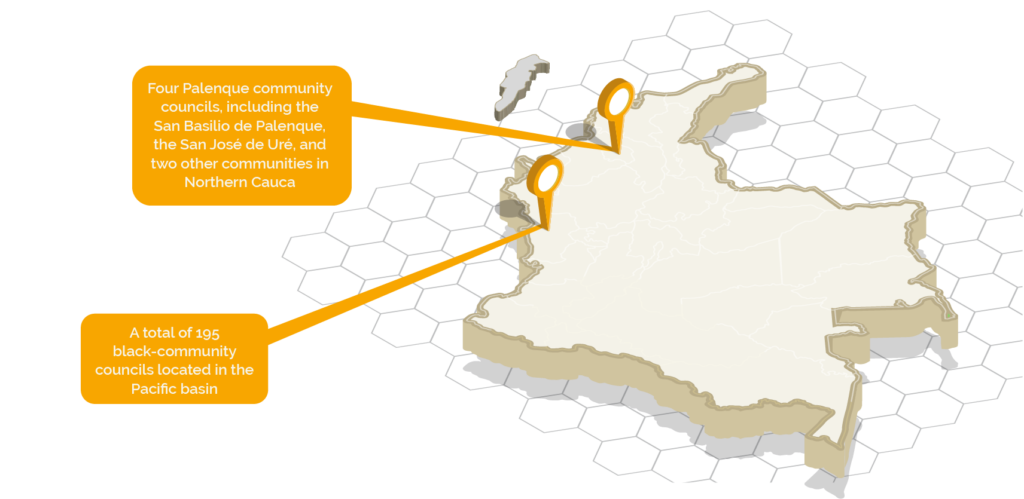


The underlying territories of the construction of the culture and identity of these communities are called community councils. So far, the following councils have been identified:


